
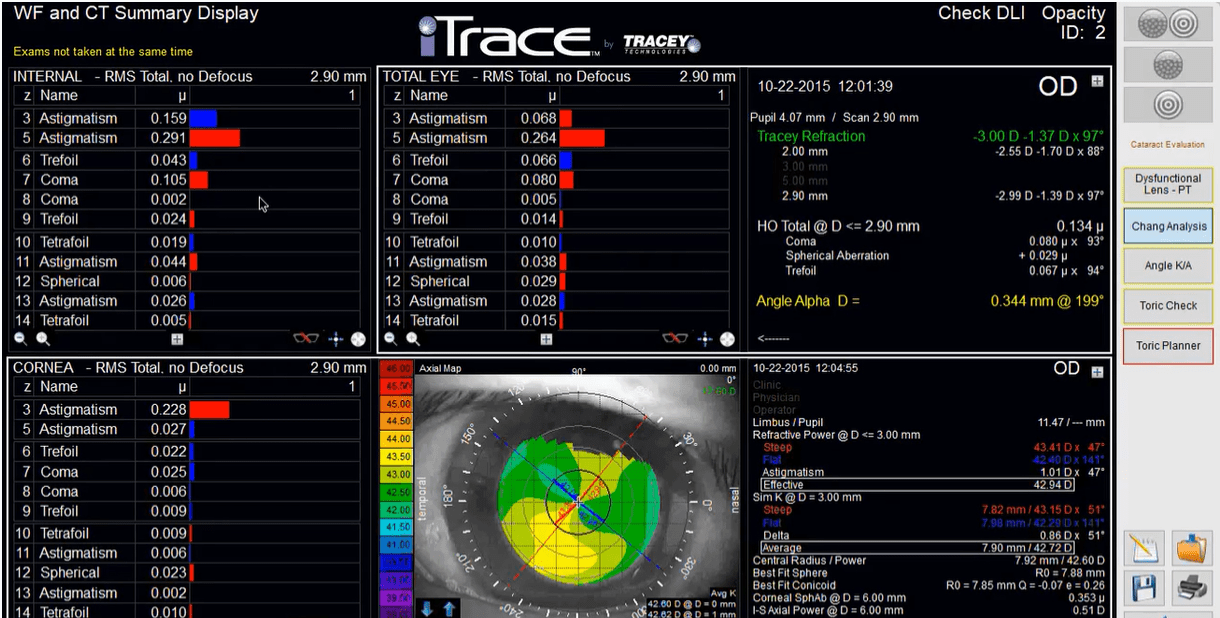
We implement and evaluate HCF in the Linux kernel, demonstrating its effectiveness with experimental measurements. Through analysis using network measurement data, we show that HCF can identify close to 90% of spoofed IP packets, and then discard them with little collateral damage. HCF is easy to deploy, as it does not require any support from the underlying network. Based on this observation, we present a novel filtering technique, called Hop-Count Filtering (HCF)-which builds an accurate IP-to-hop-count (IP2HC) mapping table-to detect and discard spoofed IP packets. Other uses: path characterization asymmetric route detection incoming.
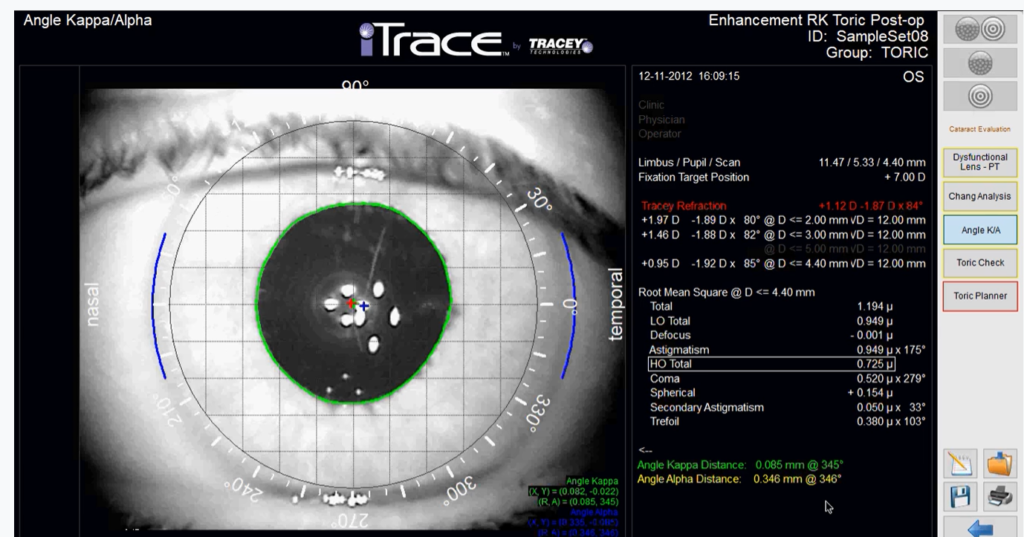
Bellovin, ICMP Traceback Messages, Internet Draft, March, 2001. Using a mapping between IP addresses and their hop-counts, the server can distinguish spoofed IP packets from legitimate ones. Primary motive: trace back denialof service attacks. ICMP traceback (iTrace) is currently being considered as an industry. On the other hand, an Internet server can easily infer the hop-count information from the Time-to-Live (TTL) field of the IP header. The ICMP packets contain information about the marking router. 7 Vern Paxson, Steve Bellovin, Sally Floyd and Ratul. The attack may be mitigated by selecting a router along the detected path and requesting the router to alter its handling of the data traffic. Routers send ICMP packets, along with the attack path, to another destination. difficult to trace back the attack to the actual originating host. More importantly, since the hop-count values are diverse, an attacker cannot randomly spoof IP addresses while maintaining consistent hop-counts. A Denial of Service attack received at a network node from a packet data communications network is managed by tracing the path of predominantly malicious data packets arriving at the network node. Although an attacker can forge any field in the IP header, he cannot falsify the number of hops an IP packet takes to reach its destination. Thus, the ability to filter spoofed IP packets near victim servers is essential to their own protection and prevention of becoming involuntary DoS reflectors. Gilmore, PG Neumann, RL Rivest, JI Schiller. IP spoofing has often been exploited by Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks to: 1) conceal flooding sources and dilute localities in flooding traffic, and 2) coax legitimate hosts into becoming reflectors, redirecting and amplifying flooding traffic. 4 H Abelson, RJ Anderson, SM Bellovin, J Benaloh, M Blaze, W Diffie, J.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
